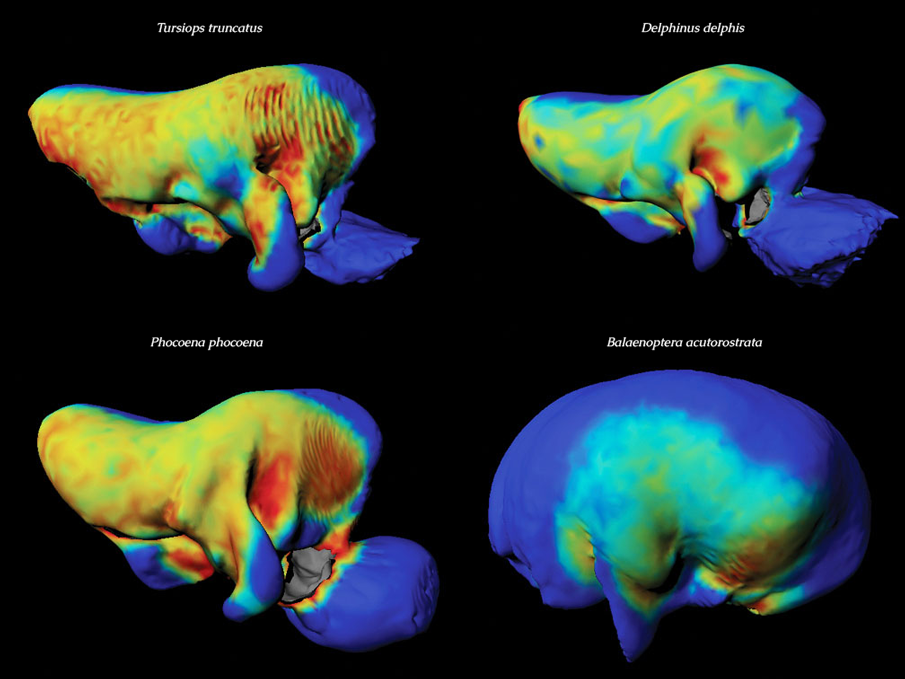
The tympanic bones are an integral part of hearing in whales and dolphins. Yet, due to the bones’ convoluted structure, it is not easy to determine how sound energy is transmitted through them. This piece shows anatomical reconstructions of the tympanic bones of four cetacean species (upper left, bottlenose dolphin; upper right, common dolphin; lower left, harbor porpoise; lower right, minke whale) color-coded by relative thickness (red = thinnest, blue = thickest). The bone is thinnest around the region where the soft tissue structure homologous to the eardrum attaches.
The anatomical reconstructions were based off of CT scans supplied by Boston University and Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. The color coding was assigned to the surfaces of the reconstructions using MEL.

